Enhancing Urban Green
Remote Control for Public Green Spaces
Enhancing Urban Green
Remote AI can be utilized for remotely monitoring and assessing the health of urban green areas, facilitating the planning of precise interventions and offering an objective evaluation of their status.
Enhancing Urban Ecosystems with Advanced Analysis
Our tailored services leverage comprehensive insights from remote sensing data, enabling thorough analysis of urban green spaces vegetation health, environmental factors, and land use.
Through the integration of deep learning data, our service, Remote AI, not only enhances the vitality and management of urban forestry and arboriculture but also estimates and mitigates the environmental impact of various activities on the surrounding territory.

Streamlined Operations
Our service optimizes public green health monitoring, minimizing personnel and manual inspection time.
Cost Efficiency
Leveraging advanced technologies reduces costs and inefficiencies, ensuring timely issue detection.

Prompt Diagnosis
Our approach facilitates quick diagnosis, preventing delays and preserving public green space value.

Sustainable Impact
Efficient monitoring and intervention promote healthier urban environments.
Dashboard Contents Overview
A Deep Dive into Dashboard Components

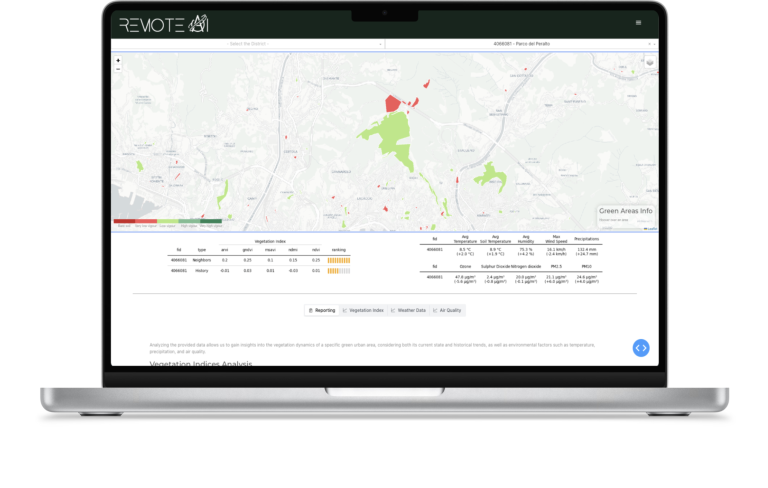
Geographical Visualization and Details of Urban Green Areas
Displays the geographical location of urban green areas and provides details such as name, area, municipality, etc.
Analysis of Vegetation Indices Over Time and Comparison Across Urban Green Areas
Observes changes over time in one or more vegetation indices within the same urban green area.
Compares the values of a single vegetation index across selected urban green areas and analyzes variability compared to other urban green areas.
Inclusion of information regarding certain meteorological and air quality data.
Dashboard Insights for Urban Green Space Analysis
Comparison of Vegetation Indices in a Single Urban Green Area
Plant Health Monitoring
Observe plant health and study their responses to climate shifts, air pollution, sunlight exposure, and other factors in urban green areas using vegetation indices.
Management Evaluation
Analyze vegetation index variations to assess green space management effectiveness and adjust practices as needed for irrigation, pruning, fertilization, or pest control.
Resource Management
Use vegetation index data for resource allocation, park design, and biodiversity conservation policies in urban planning.
Comparing Vegetation Index Across Multiple Green Areas
Environmental Quality Assessment
Analyze vegetation index variations to assess green space management effectiveness and adjust practices as needed for irrigation, pruning, fertilization, or pest control.
Management Practices Monitoring
Comparing indices assesses urban green area management. Contrasting park indices reveals maintenance, irrigation, fertilizer, or waste management differences, guiding improvement.
Identifying Critical
Areas
Differences in nearby green areas' indices may indicate issues like inadequate irrigation, soil degradation, plant diseases, or pollution.
Vegetative Indices
Monitoring Green Health

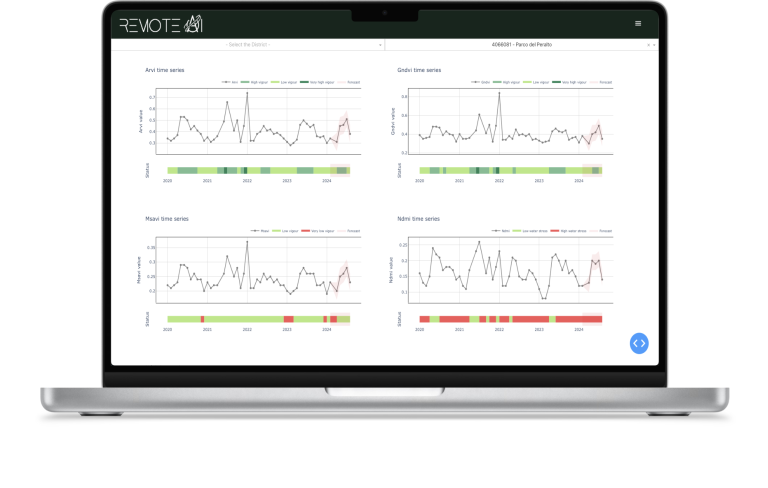
Health Monitoring (NDVI and ARVI)
These indices help monitor the health of urban vegetation, detecting stress in parks and green roofs to enable timely care.
Irrigation Management (NDMI)
NDMI assesses moisture levels, aiding efficient water management in urban green spaces to prevent waste.
Land Cover Mapping (MSAVI)
Useful in urban planning, MSAVI identifies vegetated vs. non-vegetated areas, highlighting potential locations for new green spaces.
Photosynthesis Monitoring (GNDVI)
GNDVI tracks photosynthetic activity, useful for managing and selecting plants that optimize carbon dioxide capture, thus improving air quality.
Pollution Impact Assessment (ARVI)
ARVI evaluates how urban pollution affects vegetation, guiding strategies like introducing pollution-resistant plant species or green barriers.
Enhancing Urban Green Space Management with Climate and Air Quality Data
Monitoring Green Health
Incorporating meteorological and air quality data is crucial for understanding the environmental dynamics within urban green spaces. Here are three essential uses of historical data related to air and climate quality that can significantly enhance our understanding and management of these areas:
Causal Relationships Understanding
The inclusion of climate and air quality data allows for an examination of the cause-effect relationships between environmental conditions and the health of green areas. For instance, evaluating how climate variations or air pollutants influence plant growth, local biodiversity, or the presence of sensitive species.
Ecological Vulnerability Assessment
By analyzing climate and air quality data alongside green area health indices, vulnerabilities of ecosystems to environmental changes can be identified. This is particularly vital in the context of climate change, enabling prediction and mitigation of negative impacts on natural resources and ecosystems.
Management Decision
Support
Climate and air quality data provide a scientific foundation for green area management decisions. For example, they can inform irrigation strategies, the selection of plant species to use, or actions to improve air quality in the surrounding environment.
Urban Green
Insights in Italy
The 2021 Istat surveys provide key insights into Italy’s urban green spaces. With an average of 32.5 square meters per inhabitant, it emphasizes their significance in urban landscapes. In provincial capitals, there’s an average of 15 square meters per inhabitant, indicating the need for equitable access. Additionally, the data on trees per 100 inhabitants underscores variations in urban forest management. These insights inform policy and urban planning for sustainable city development.
